Horizontal machining is a powerful tool for creating complex parts and components. It is used in a variety of industries such as automotive, aerospace, medicine, and others. With its wide range of cutting tools and automated options, it can be a powerful asset to any manufacturing team.
Horizontal machining, also known as milling, is a process in which a workshop machines a part while it is held horizontally in place. This type of machining is used to create components and parts with precise shapes and dimensions that can be used in manufacturing.
The horizontal machining tool is made up of a large table, called the worktable, that holds the raw material in place. Attached to the table are several spindles—called cutters—that are used to cut away and shape the material into the desired form. The spindles are connected to rotating arms that control the movement and cutting speed of the tool.
The table can also be fitted with tools such as drill presses, lathes, and taps for finer detailing. These tools allow for the precision machining of components down to fractions of an inch in size. Horizontal machining centers also feature computerized numerical control (CNC) programming for complex geometries that require intricate shapes or contours.
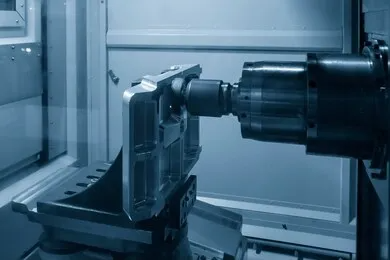
Horizontal machining involves the use of cutting tools that are positioned horizontally and move on an X, Y, and Z-axis. At its core, there are three major components to a horizontal machine: the spindle, the table, and the cutting tool.
The spindle is part of the machine that rotates and houses the cutting tool. It is this rotation that powers the cutting action of any horizontal machining operation. The table holds the workpiece in place while it is being machined and can move both horizontally (X-axis) and vertically (Y-axis). The cutting tool is generally driven by a motor or power source, such as a hydraulic or electric system, which allows it to make precise movements in three directions (X-Y-Z axes).
By understanding these three components –spindle, table, and cutting tool—you’ll have a better understanding of how a horizontal machining center works. Additionally, having an understanding of these components will go a long way in helping you to get more out of your machine and maximize its efficiency for any given project.
Whether for large or small-scale production, many horizontal machining tools are available, each designed to serve different purposes. Here’s a quick overview of the most common tools used in horizontal machining:
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Mills are the most commonly used type of horizontal machining center, and they employ a cutting tool that is driven by a spindle along either X, Y, or Z-axis. CNC Mills come in various sizes and styles to facilitate different types of operations.
Horizontal lathes are designed to spin cylindrical pieces of metal at high speeds, allowing for precise cuts and surface finishes. They typically come with a chuck and a tool post that can be adjusted to achieve intricate designs with ease.
Drilling machines are another important type of horizontal machining tool used for cutting holes into workpieces with maximum precision and accuracy. They are commonly equipped with multi-spindle heads that allow for multiple drills to be installed simultaneously for faster productivity.
By understanding the basics of these three common types of horizontal machining tools, you can make an informed decision on which one is best suited for your needs. With regular maintenance and proper usage, these machines can become highly effective assets in your manufacturing processes.
Horizontal machining is rapidly becoming one of the most popular machining processes. That’s because it offers several advantages over traditional vertical machining processes, such as increased efficiency and better utilization of space. Here are a few key differences between horizontal and vertical machines:

The spindle on a horizontal machine is positioned horizontally, while the spindle on a vertical machine is positioned vertically. This allows for more efficient cutting with a horizontal machine since the cutters are parallel to the surface.
The axis of motion for a horizontal machine is left-right, while the axis of motion for a vertical machine is up-down. This difference allows a horizontal machine to access more areas due to its wider range of movement.
The cutter position on a horizontal machine is at the side or below the workpiece, while the cutter position on a vertical machine will typically be above the workpiece. This ensures that chips are removed from both sides of the workpiece when machining with a horizontal machine.
With these differences in mind, it’s easy to see why so many manufacturers are opting for horizontal machines over their vertical counterparts. The increased accuracy combined with improved access makes them ideal for nearly any machining task.
Horizontal machining is an essential tool for a successful CNC machine shop. CNC horizontal machines offer numerous advantages over traditional vertical machines, including higher accuracy and precision, faster speeds, and improved productivity.
One of the primary advantages of CNC horizontal machines is their superior accuracy and precision. Due to their rigid construction, they can achieve tight tolerance requirements on even the most intricate parts. This makes them ideal for processing lightweight aluminum components as well as heavier materials such as steel and titanium.
CNC horizontal machines are also able to run at faster speeds than vertical machines due to their flat construction—which makes them better suited for large production runs where time efficiency is a priority.
CNC horizontal machines are highly productive tools that enable users to quickly set up jobs and complete machining tasks in less time than traditional vertical machines. This improved productivity makes them ideal for meeting tight deadlines without sacrificing the quality or accuracy of the finished product.
As with any tool, horizontal CNCs come in many different configurations to suit the specific needs of various applications. The two primary categories are floor-mounted and table-mounted. Both can perform the same operations but differ in terms of their setup and installation.
The floor-mounted model is held to the ground by a set of anchors and can be accessed from all sides. This type of machine offers increased stability and is often used in heavy-duty applications that require precise cuts. The large size allows for the addition of multiple spindles, providing flexibility when taking on complex projects.
The table-mounted configuration mounts directly to a sturdy table or base, which provides support. This type of machine is more compact than its floor-mounted counterpart and is often used for short runs or one-off pieces due to its smaller bed size and lack of flexibility in configuration options. However, depending on the application, it can be extremely precise.
Horizontal CNC machines are a valuable tool in any machining shop, with the ability to tackle most milling and boring operations. Horizontal machines come in three main varieties: floor-milling machines, bed-type milling machines, and machining centers. The right kind of machine for you depends on the type of work you plan to do and the space available in your shop.
Floor milling machines are large, free-standing machine tools that have a column-and-knee design. They usually have a manual overhead head with a quill that can move up and down for drilling and boring. Floor milling machines are ideal for heavy parts that require more rugged cutting, such as larger blocks of material or heat-treated castings.

Bed-type milling machines are also free-standing, but they feature a more compact footprint than floor milling machines. They also have a long cross slide to increase their capacity for heavier parts. Bed-type mills typically have a vertical spindle head with an adjustable or fixed quill feed rate, so they’re best suited for precision production tasks.
Machining centers feature an all-inclusive design that integrates several machining processes into one machine tool — such as 3D contouring and drilling, slotting, and tapping — all while minimizing movement between operations. This added versatility makes machining centers ideal for production runs or limited production tasks where repeatability is key.
Before you can begin to master horizontal machining, it is important to understand the different types of movement and coordinates on a 5-axis CNC Horizontal Machine.
The movement axis of a 5-axis CNC Horizontal Machine is the X, Y, Z, A, and B axes. The X-axis is used for left/right movements, Y for forward/backward movements, and Z for up/down movements. The A and B axes are used for tilting the tool and workpiece in any direction along with X, Y, and Z axes.
The coordinates of a 5-axis CNC Horizontal Machine refer to the location of the tool or workpiece relative to its origin point. The coordinates that can be specified by the user are X0, Y0, Z0 (origin), A0, and B0 (tilt angles). All these coordinates are called absolute coordinates because they refer to an absolute position within a 3D space relative to its origin point.
By understanding the different axis movements and coordinates involved in horizontal machining, you will be better prepared to start mastering this complex process. With practice and experience, you'll be running complex jobs in no time!
Horizontal machining tools can be used for a variety of tasks, including drilling, boring, and tapping. These tools are most commonly used in metalworking applications, including milling, turning, and reaming. They can also be used in other materials such as plastics and composites.
Furthermore, horizontal machining centers are frequently used to produce custom parts from a variety of materials. For instance, aerospace components often require precise tolerances and must be machined with high accuracy for optimal results. This is where horizontal machining centers come into play—they provide the accuracy needed to ensure that parts meet tight specifications.
In addition to aerospace components, horizontal machines are also ideal for producing molds and die for plastic injection molding machines. With their low cost and high precision compared to other types of machine tools, they are an excellent choice for producing molds and dies in short runs or small production runs.
Finally, horizontal machining centers are ideal for producing large-scale parts due to their increased rigidity over vertical machines. This rigidity helps minimize vibration during the machining process; thus reducing potential errors while increasing the accuracy and quality of the finished product.
The last decade has seen tremendous advances in the technology of horizontal machining with the introduction of computer numerical control (CNC) systems, as well as the development of more precise spindles and motors. This has enabled faster, more precise machining and improved cutting accuracy, as well as lower operating costs.
These advances are not only helping to reduce costs, but they are also allowing manufacturers to create intricate parts with more complex geometries and higher tolerance levels than ever before. For example, CNC systems have made it easier and more cost-effective to produce parts with intricate designs, such as turbine blades, turbine nozzle segments, and impellers for aircraft and industrial applications.
As these technologies continue to develop, manufacturers can reduce the amount of time and money spent on each part by increasing the speed and accuracy of the machining process. This in turn results in higher quality parts and faster production times, creating a positive feedback loop that helps to drive the cost savings associated with horizontal machining.
These advances are also having a positive effect on the environment, as they enable manufacturers to reduce their output of harmful gases as a result of the improved efficiency associated with the use of horizontal machining. This helps to reduce the carbon footprint of many industries around the world, and it is helping to create a more sustainable future.

In conclusion, horizontal machining is a powerful technique that can be used to create precise and accurate components. With the right machine and technique, horizontal machining can deliver greater productivity than vertical machining, while still offering the same end-product features. The technology is continuously evolving and can be used in a range of industries, from aerospace to automotive.
Whether you are an experienced machinist or are looking to get into CNC machining, mastering the basics of horizontal machining is the first step in achieving the best results. Knowing the correct techniques, the right machines, and the appropriate materials will help you to achieve the highest quality components for your customers.