A complete CNC machining process relies on a well-designed tooling system to ensure efficiency, accuracy, and productivity.
CNC tooling systems integrate cutting tools, tool holders, and adapters to streamline tool selection, reduce setup time, and support stable machining operations. By using standardized tooling modules, machining centers can perform a wide range of cutting tasks while minimizing downtime, cost, and operational risk.
Understanding how to select and configure the right cutting tools and tool holders is essential for maintaining an efficient CNC machining cycle.
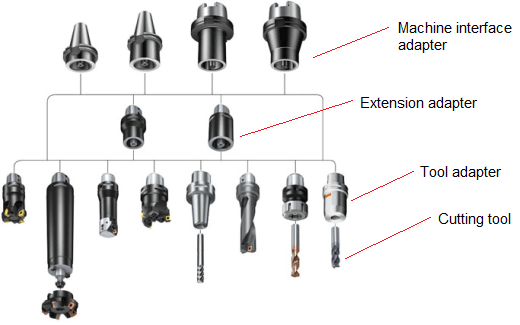
A tooling system for a machining center is a complete combination of cutting tools, tool holders, tool interfaces, and tool management components that enable a CNC machining center to perform milling, drilling, tapping, and boring operations accurately and efficiently.
Unlike standalone cutting tools, a tooling system focuses on rigidity, repeatability, tool change speed, and machining stability, which are critical for modern CNC machining centers operating in batch or continuous production.
A well-designed tooling system directly affects:
Machining accuracy
Surface finish quality
Tool life and cost
Machine uptime and productivity
Your machining success lies in the tooling system. Check the checklist below to machine parts effectively.
It's essential to look for the properties of the tool before selection. For instance, if you want a tool that has long-term life and resists high heat, the best tools you may use are high-speed steel tools. However, for cutting away extra hard materials like cast iron, opt for cutting ceramics.
The flute number indicates the feed rate or velocity of the cutter on the material. Tools should have a moderate number of flutes, as there are too many tears off workpiece bits.
The coating of your tool impacts the process. Coating increases or decreases production costs. So, choose wisely.
Before starting the cutting process, understand the machining systems.
Consider the following Machine parameters to obtain your desired results:
• Machining output
• Spindle Clamping options
• Tooling system
As the material is machined, the surface quality, abrasiveness, and finishings are maintained through a dust collection setup. Understand the properties of cutting tools for proper selection. That's what leads to expected feed capacity and cost efficiency. Tooling contributes to a cost-effective production.
You might have noticed steep tapers or HSK tool holders in wood, plastics, and composite-made CNC machining centers. Such tooling holders produce quality products through high levels of accuracy. You won't see any uneven or rough surface, but a smooth one up to the finest detail.
Furthermore, tool holders are equipped with ball-bearing collet nuts. Though it's the best option, some cnc machining manufacturers even supply a single static nut to the system. Ball-bearing collet nuts don't couple the inner rings nut. Thus, a circular motion of the ball bearing generates a clamping force.

There's a variety of modular tool holders, including collet chucks, heat shrink, and hydro holders for most advanced machining applications. Let's discuss each holder and its benefits:
If you want to execute high-speed machining operations, a heat-shrink tool holder is the best choice. Tool holders are placed on a heat-shrink chuck. You'll not have to use a collet system.
Besides this, you have the option to mount the heating equipment on the tool shank. However, it requires a cost investment to replace the tool from the chuck. Inserting a carbide tooling system allows manufacturers to set the tools and store them in one place.
Another choice to reduce pressure or tolerance between machine systems and tools is a hydro chuck tool holder. These are available in metric sizes ranging from 10mm to 25mm.
When you have cutting tools, there's no need to spend initial costs on tools. Choosing the right tool is important. Poor quality tools aren't capable of performing the function, thus limiting the machining process and costing far more.
Here's different tools you need to know:
• Solid carbide spiral tools
• Insert tools
• Custom profile tools
• Polycrystalline diamond (PCD) tooling
Buy accurate tool holders and cutting tool selection to ensure high-quality finishing, accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and waste reduction. That's how you maintain the integrity of your machine.
If you get a carbide-tipped bit for a CNC machine, it won't maintain uniformity. However, insert tools are preferred to maintain the dimensional accuracy at a low expense.
When running polycrystalline diamond (PCD) through the machine having a phenolic fabricator with carbide bits, it'll minimize machining costs.
Tooling basics include tool holders, cutting tools, and their use in vertical machining centers. If this tooling is faulty or inaccurate, the production won't go far.
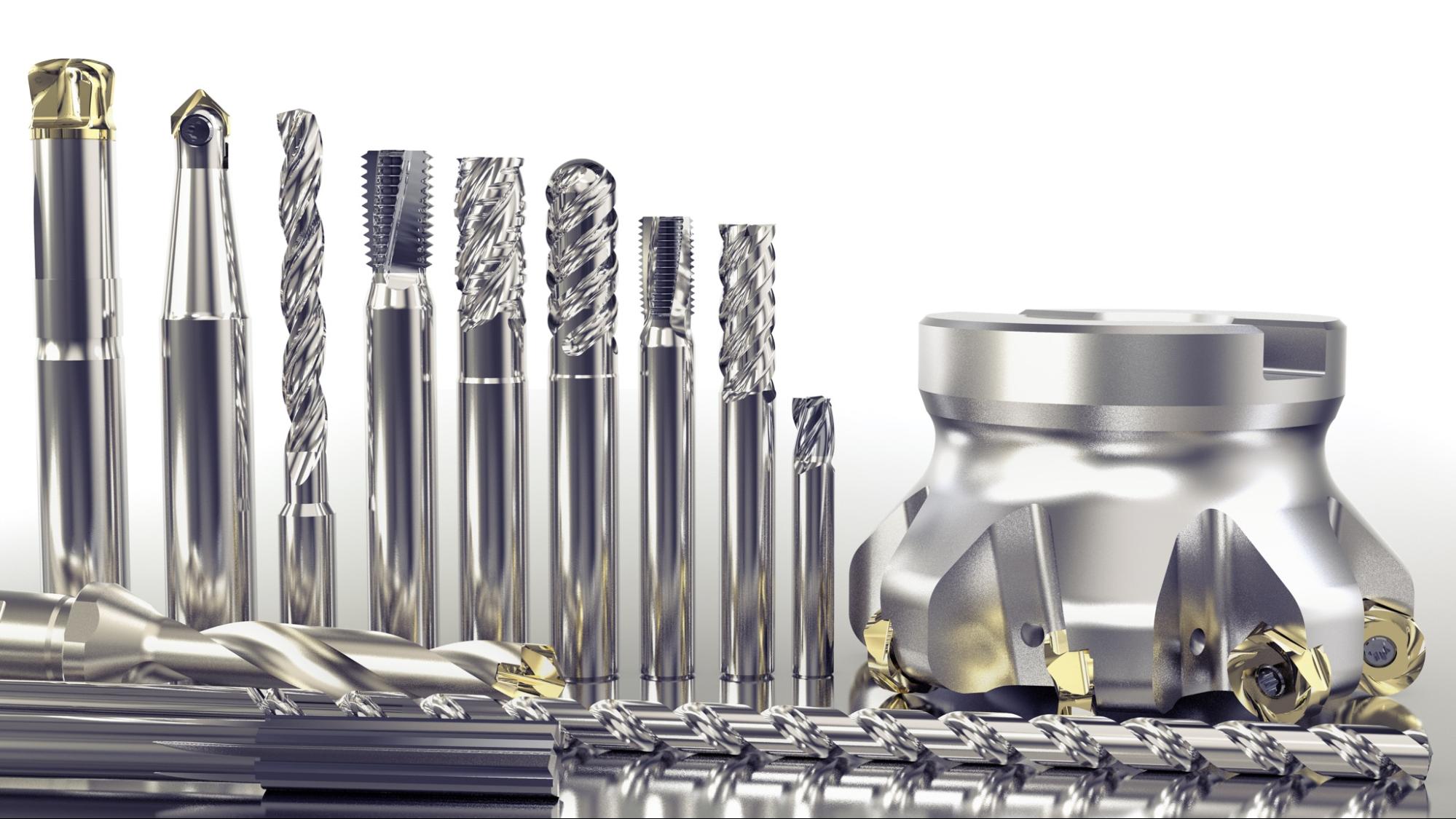

Conical cutting points and helical grooves make up the drill bits. There are three varieties of drill bits:
• Center drill bits
• Twist drill bits
• Ejector drill bits
Drilling the workpiece to create small points is possible with center drill bits and developing precise spots using twist drills. Besides, ejector drills help make deep holes.
There comes a much more versatile option than drill bits and end mills. It's eight flutes specifically for removing materials without pre-drilling in the minimum time.

Before milling the workpiece, you have to prepare the initial material for the next phase. Face mills insert multiple cutters to create flat sections of the pre-material.
For complex operations, both side and face cutters are used to cut grooves along with the sidewalls of the workpiece.
Another important cutter in the horizontal CNC machining center is the gear cutter. These include angle, screw, and spur for manufacturing products.
Create a perfect pre-thread diameter using hollow mills. This cutting tool has more than 3 cutting tools to move around the workpiece for finishing projections.
When you need to cut internal or external threads, fix thread mills in your machine's tooling system. Also, penetrates metallic parts through thread mills.
Making wide and narrow cuts on flat surfaces is easy through slab cutters or slab mills. This tool for cutting teeth on the periphery is an ideal choice for quick cuts.
If you want to make shallow cuts on materials, these rotary tools can produce smooth surfaces. It's a go-to tool for anyone tight on budget.
When the cutting process ends, grinding begins. Grinding tools and wheels work together to produce a high-accuracy workpiece.

When you have drilled the workpiece, enlarge holes through boring tools. A lathe is used with boring tools to taper holes.
Refining or smoothing the workpiece's sharp edges is crucial. That's done using chamfering tools. Also, perform deburring and bevelling.
These tools turn a simple material into unique geometric patterns such as straight, diagonal, and diamond. These shapes or patterns on workpiece surfaces provide better grip and finishing to the material.
A parting tool with a sharp blade edge plays its role in cutting materials from the workpiece. These tools may also be used to cut away the finished part from leftover workpieces.
After choosing the tools for your machining process, you should know how to use them. Every tool is designed with specific parameters. So, performing cutting within the parameters provides accuracy.
For proper cutting, the cutting tools' performance doesn't matter. But there's a need to check the machine integrity, materials strength, dust extraction, clamping system, tool holders (collets), and machining parameters.
In addition, chip load is another factor to consider. During the cutting period, you have to note the chip load that should be in an ideal range. If the chip load doesn't meet the ideal, the tools overheat, and the tooling system lifetime decreases, thus affecting the machining process. Using tools beyond their limit causes the tools to break.
One of the prominent parts for better cutting through the tooling system is running the cutting edge over the material at the right speed. Even the flute routing bits can't yield better results. Only the chip load is responsible for the CNC machining tooling systems' quality, efficiency, and tool life.
It's the thickness or size of the chip that is reduced when edges are cut in each revolution of the tool. Shifting from a 2-flute bit to a 3-flute bit reduces 33% chip size if the rate is not adjusted accordingly. Smaller chips cause more heat production as the chip cannot be extracted with a single cut and is recut into tiny particles.
Chip load charts provided by the manufacturers or online are assumed as the reference point, and it depends on the user whether to look for a sweet spot that offers long-term tool service, finishing, and cost.
Here's the chip load formula
Chip Load = Feed Rate (inches per minute) / (RPM x number of flutes)
For instance, Chip load = Feed Rate 600"/minute /(18,000x2 flutes) C600 Load = 0.017"
Increasing the size of the chip may decrease the quality of the cut. Similarly, a decrease in chip size can shorten the tool's lifetime. Therefore, look for the ideal middle option to optimize both finishing and tool life.
There exist two types of cutting directions: climb cut and conventional cut. In climb cutting, feed, and cutting edge are in the same direction. Never execute manual operations, as matching material might kick back; that's dangerous. Climb cutting is a preferable choice due to high-quality product finishing.
On the other hand, feeding takes place in the opposite direction to the cutting edge in conventional cutting. Hence, cutting tools exert less pressure on cutting and boost tools' lifespan.
Employing the latest high-quality CNC machine tools is the most critical step. The tooling system ensures your project runs smoothly.
CNC tooling and inventory systems enclose many advantages, including optimized tool life, lower equipment costs, ideal performance, improved efficiency due to enhanced setup, changeover time, and high-quality production.
Willing to get precise cuts on your material? High-quality tools can do the job. So, you can meet your product's specifications and requirements through tools. So get the best one.
Saving time is an essential factor in the machining Industry since manufacturers have to produce tons of products. You need precise cutting and finishing. Here's where the right tools deliver products on time. So, save your recutting time with tools ensuring accuracy.
Product finishing is what matters. Using outdated tooling won't give the desired results, causing jagged edges and imperfections. Therefore, keep updating your tooling system to produce a smooth finish.
Whether it's solid-grade laminate or styrofoam sheets, 3 and 5-axis cuts and machine materials on a CNC router are available for a variety of applications.
Tools should also ensure dimensional accuracy, so there's minor or no deviation and your project fits your specifications.

From choosing the right tooling system to using different cutting tools, you've got valuable insights for CNC machines. Apart from the above factors, you'll also have to keep some other considerations in mind.
Here are additional factors to keep an eye on:
• Design geometric patterns or complexity
• Materials quality
• Surface finishing
• Material tolerance range
• Tooling systems accuracy
Sometimes, one cutting tool is enough, but other times, you require a complete tooling system to get the work done. It all depends on the material at work.
1. What is a tooling system in a CNC machining center?
A tooling system in a CNC machining center refers to the complete combination of cutting tools, tool holders, adapters, and interfaces used to perform machining operations.
Its purpose is to ensure accurate tool positioning, stable cutting performance, and efficient tool changes, rather than simply holding a cutting tool.
2. Why is a tooling system important for CNC machining?
A proper tooling system directly affects:
Machining accuracy and surface finish
Tool life and cutting stability
Setup time and production efficiency
Without a suitable tooling system, even a high-performance CNC machine cannot achieve consistent or repeatable results.
3. What components are included in a CNC tooling system?
A complete tooling system typically includes:
Cutting tools (end mills, drills, taps, boring tools)
Tool holders (collet chucks, hydraulic chucks, shrink fit holders)
Tool adapters and extensions
Machine spindle interfaces (BT, CAT, HSK)
Tool measurement and presetting devices
Automatic Tool Changer (ATC) compatibility
Each component plays a role in maintaining machining accuracy and workflow efficiency.
4. How do tool holders affect machining performance?
Tool holders determine clamping force, runout, and vibration control.
Poor-quality or mismatched tool holders can cause:
Chatter and vibration
Reduced surface finish quality
Premature tool wear
Selecting the right tool holder improves cutting stability and extends tool life, especially in high-speed or heavy-cutting applications.
5. How does an automatic tool changer (ATC) work with the tooling system?
The ATC stores pre-assembled tools in a magazine and automatically exchanges them during machining cycles.
A compatible tooling system ensures:
Reliable tool gripping
Accurate tool positioning after each change
Reduced machine downtime and manual intervention
6. How to Choose the Right Tooling System for Your Machining Center?
When selecting a tooling system, consider:
Machine spindle type and speed range
Workpiece material and hardness
Required machining accuracy
Production volume (single piece vs batch)
Tool change frequency
Matching tooling capability with machine performance ensures stable and efficient production.
Tooling systems and cutting tools have great importance in CNC machining centers since they optimize and boost system capacity, reduce waste production, provide efficiency, and save cost.
Without quality tools and equipment, high-quality products aren't possible. So, before you set up a tooling system, it's necessary to understand the basics of tools. Have a close look at the pros and cons of each tooling system by researching and understanding the functionality.