Angle milling heads are the very heart of advanced production; they create precision itself. In this blog, 'Mastering Angle Milling Heads: In our book ‘A Guide to Advanced Manufacturing,’ we go deeper.
Our exploration is exhaustive and includes types, applications, and setup approaches. Our goal is to make complex ideas clear and uncomplicated.
Every part is interspersed with technicalities very easily making expertise approachable. Have a pleasant tour of the precision mechanics.
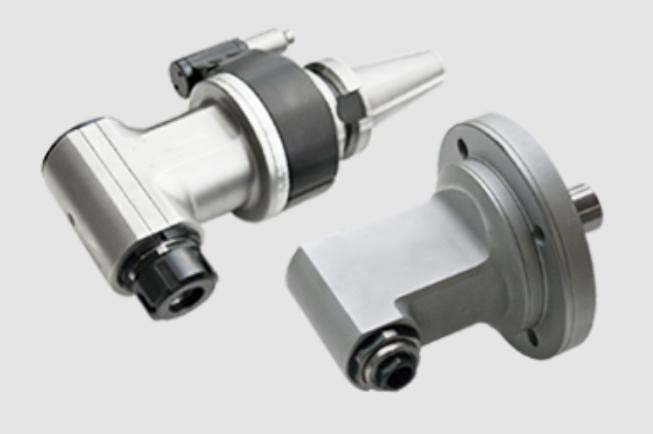

The role of angle milling heads in the machining process is to make possible the accuracy and efficiency of creating angular cuts and details on workpieces. This guide looks at various types of angle milling heads, their uses, and technical details associated with each type.
Cutting angles are made in workpiece by single-angle cutters. They are constructed to create chamfer angles, primarily utilized in chamfering, beveling and weld seam preparation activities.
The size of the cutting face and the edge angle of these cutters can differ, and the latter characteristic is very important for the machinists to get the right precision in their projects.
A double-angle cutter is defined by two angled surfaces, which come together at the tip. They are used mostly for complicated operations such as grooving, threading, and V-groove milling.
Dual angles provide flexibility in machining operations therefore they are the strategic tool in complex angular cuts machining tasks.
The adjustable angle milling heads offer flexibility and adjustability for custom and precision machining operations. Adjustable head of these heads can be set to different angles due to what a machinist can use one tool for several angle cuts, which is rather useful for improving the workflow and decreasing tool changeover time.
Fixed angle milling heads are characterized by a fixed angle, often used for such tasks that require the same angle to be constant all the time. They guarantee the toughness and reliability, in this way the angle is preserved and unchanged during the grinding process, providing precision in mass production.
|
Feature |
Single-Angle Cutters |
Double-Angle Cutters |
Adjustable Heads |
Fixed Heads |
|
Cutting Angles |
45° to 90° |
30° to 120° |
Varies |
Fixed |
|
Applications |
Slotting, Chamfering |
Back chamfers, V-grooves |
Diverse |
Specific |
|
Material Type |
HSS, Carbide |
HSS, Carbide |
HSS, Carbide |
HSS, Carbide |
|
Flexibility |
Low |
Moderate |
High |
None |
|
Setup Time |
Short |
Short |
Long |
Shortest |
|
Accuracy |
High |
High |
Adjustable |
Highest |
Table on Types of Angle Milling Heads!
The material of angle milling cutters is of high importance defining their performance and applicability for various machining tasks. Typical materials that offer various levels of hardness, resistance to heat, and long life are high-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and cobalt.
The number of flutes, shape of cutting edges, and helix angle define the geometry of angle milling cutters and are crucial for the cutter performance. Characteristic shapes define the cutter’s efficiency in chip removal, heat control, and general cutting quality.
Angle milling cutters are often coated in substances like titanium nitride (TiN) or aluminum titanium nitride (AlTiN) to improve their hardness and resistance to wear and heat. The coatings enhance the life of the tool and its performance at high speeds.
Angle milling cutters are available in different sizes, which are chosen depending on the particular need of the task and the material to be machined. The cutter diameter and length should be appropriate for the milling machine’s references and sizes of the workpiece.
Correct positioning of the angle milling heads is very important in obtaining the exact and clean cuts. The misalignment might result in differences in machining and excessive wear of the tool and the possible destruction of the work piece. Hence, alignment should be checked and adjusted regularly.
Calibration of angle milling equipment guarantees that the machine works within the tolerances set. This operation is very important for controlling cuts precision and the overall quality of machined parts.
The right tool for angle milling is chosen based on the workpiece material, type of cut, and the capabilities of the milling machine. Correct tool choice is crucial for productive and quality machining.
Having the Adjustment of the milling operation speed is very important for the cutting process optimization. Various materials and kinds of cuts need different speeds to optimize the cutter’s performance and extend its life.
The feed rate in angle milling must be precisely adjusted to the properties of the material and the finish of the workpiece. Proper feed rates control can have large effect on the quality of the cut and the efficiency of the machining process.
Climb milling is the most preferable when using a cutter that rotates in the same direction of the feed due to its capability to make clean cuts and efficiently handle chips. This method also has smaller kickback and can increase the life of the cutter.
Conventional milling from the fact that the cutter rotates against the feed, is applied when use of the climb milling is impossible due to machine rigidity or backlash. Even if it can be more difficult from the point of view of chip control, there are situations when this option is required.
Helical milling is a live process in which the cutting action is carried out by helix motion of the cutter. This method is particularly suitable for thread cutting or cutting helical grooves, but needs the most careful setup and adjustment to guarantee accuracy.
On the other hand, profile milling is accomplished by shaping the external outlines or profiles of a part. This method is complicated because it needs accurate tool paths and sometimes also multiple passes to get the proper profile correctly.

The knowledge of fundamentals of G-code, the language for programming CNC machines is crucial in order to prepare and launch angle milling operations. G-code controls the movement of the machine, the speed it is cutting at, and the directions to take.
In CNC machining, M-code is used to operate the hardware features of the machine, e.g. coolant flow or spindle speed. The optimal use of M-code is essential for improving the efficiency and safety of angle milling processes.
Simulation software helps machinists see and test their CNC programming before milling actually starts. This is a very important step in order to prevent errors and to achieve an optimal machining process.
Optimization strategies of CNC programming for an angle mill operation can substantially improve the productivity and result. Tactics could include modification of cutting routes, change of speed and feed, and the introduction of advanced tooling solutions.
CNC machines make modern milling operations possible. They offer the accuracy and manageability that is required to perform difficult bevel cuts and guarantee the quality of machining works.
Milling cutters are essential instruments in angle milling, aimed to accomplish different cutting functions. The cutters selected according to the job needs are fundamental to the success.
Workholding devices are devices that keep the workpiece steady when the mill is in operation. The correctly chosen and installed devices are required to guarantee precision and absence of movement or slipping during the cutting.
The coolant systems act a critical part in controlling the temperature during milling operations. They aid in heat control, decrease tool wearing, and enhance the surface quality by rinsing away chips and cooling the cutting zone.
Deflection of the tool may occur during milling, which influences the precision of the cut. Among factors causing deflection, tool length, diameter, and material should be mentioned. The factors that affect these are to be understood and managed for the preservation of accuracy.
Heat control during milling is important enough to avoid the damage of tool and/or the workpiece. Efficient heat control leads to longer tool life and better finishing quality.
The achievement of a high-quality surface finish is dependent on the accurate regulation of milling parameters and the tool state. Surface finish is an important factor in relation to both aesthetic and functional aspects of a machined part.
The MRR must be optimized to achieve efficiency without compromise on quality. Increased MRR may accelerate the production time but can cause surface finish and tool life to suffer.
Instruments of measure like calipers, micrometers, and also CMMs (Coordinate Measuring Machines) are very important for checking the dimensions and angles of machined parts and making sure they comply with the set specifications.
The calibration of milling machines should be carried out regularly in order to ensure accuracy and precision during machining operations. Calibration is what makes the machine work as it should and create parts within allowed tolerances.
Error compensation implies fine tuning of the machine process in order to neutralize the known errors of the tool geometry or the machine functions. This tradition is a must for obtaining the ultimate accuracy in angle milling.
Angle milling process control effectiveness requires the real-time control and adjustment of the machining parameters to maintain correct performance. This involves controlling speeds, feeds, and cooling systems to ensure uniformity and quality during the entire production process.
During the comprehensive analysis of angle milling heads, we have considered different classes of them, ranging from simple single-angle cutters to multipurpose adjustable heads.
We have touched on materials, cutter geometry, and proper tool selection and setup for optimum machining results. Keep in mind that the art of angle milling heads can significantly improve your production accuracy and productivity.
For more details and advanced answers in angle milling, please visit CNCYANGSEN. Take your manufacturing capabilities to a higher level by using the advancement of angle milling heads today.